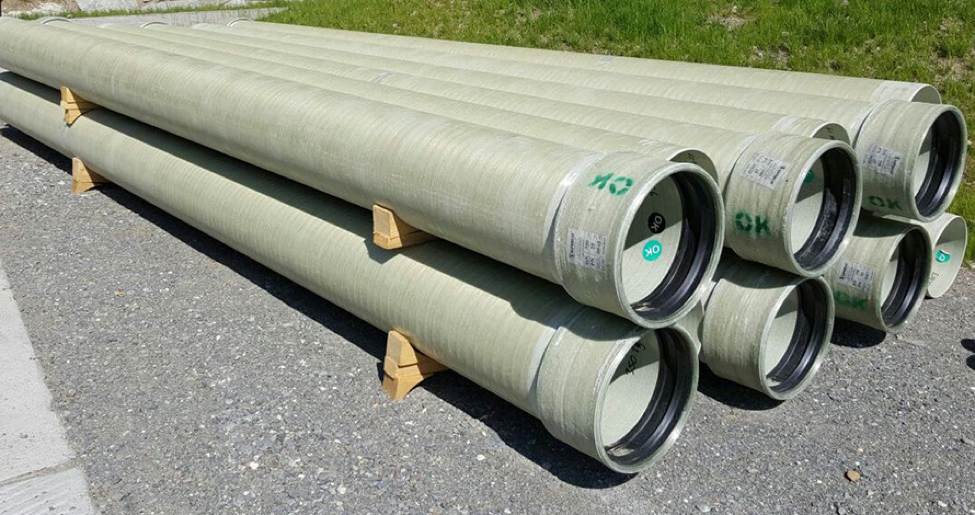
In the realm of infrastructure development and fluid transportation systems, glass-reinforced plastic (GRP) pipes stand out as a versatile and efficient solution. Engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions while offering numerous advantages over traditional materials, GRP pipes have become increasingly popular in various industries. Let’s delve into the myriad benefits of GRP and why embracing them can lead to enhanced performance and efficiency.
Understanding GRP Pipes
GRP, also known as fibreglass reinforced plastic pipes, is composed of a combination of glass fibres and thermosetting resins. This construction imparts exceptional strength, durability, and corrosion resistance to the pipes, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Pipes are renowned for their lightweight nature, ease of installation, and low maintenance requirements.
Superior Strength and Durability
One of the primary advantages of pipes is their superior strength-to-weight ratio. Despite being lightweight, pipes exhibit remarkable strength and durability, capable of withstanding high-pressure conditions and heavy loads. Unlike traditional materials such as steel or concrete, pipes do not corrode, rust, or degrade over time, ensuring long-term reliability and minimal maintenance costs.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion is a significant concern in fluid transportation systems, particularly in environments with aggressive substances or varying pH levels. Pipes offer exceptional corrosion resistance, making them ideal for transporting corrosive fluids such as acids, alkalis, and sewage. The inert nature of GRP prevents chemical reactions, ensuring the integrity of the pipeline and prolonging its service life.
Hydraulic Efficiency
GRP pipes boast smooth internal surfaces that promote efficient fluid flow with minimal friction losses. This hydraulic efficiency translates to lower pumping costs and energy consumption, contributing to overall operational savings. Additionally, the smooth bore of pipes inhibits the build-up of scale, sediment, or biofilm, reducing the risk of clogging and maintaining consistent flow rates.
Flexibility and Versatility
The inherent flexibility of GRP allows for easy customisation and installation in various configurations, including straight runs, bends, and transitions. This versatility enables engineers to design complex pipeline networks tailored to specific project requirements, thereby optimising space utilisation and minimising installation time. Whether used in water distribution, wastewater management, or industrial applications, GRP offers unmatched adaptability.
Environmental Sustainability
In an era of increasing environmental awareness, the choice of sustainable materials is paramount. GRP align with green initiatives due to their eco-friendly composition and long life cycle. Unlike materials such as PVC or concrete, which can have significant environmental impacts during production and disposal, GRP is recyclable and contributes to reducing carbon footprints.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial cost of GRP pipes may be marginally higher than that of traditional materials, their long-term cost-effectiveness is undeniable. The durability, corrosion resistance, and low maintenance requirements of GRP result in reduced lifecycle costs and fewer disruptions due to repairs or replacements. Moreover, the lightweight nature of GRP facilitates easier handling and installation, further enhancing cost savings.
Applications Across Industries
GRP find applications across a wide spectrum of industries, including water supply, irrigation, oil and gas, chemical processing, and desalination plants. Their versatility, coupled with superior performance characteristics, makes them the preferred choice for demanding environments where reliability is paramount. Whether conveying potable water to communities or transporting corrosive chemicals in industrial settings, GRP delivers consistent results.
Ensuring Longevity Through Proper Maintenance
While GRPs are renowned for their durability and low maintenance requirements, proactive upkeep is essential to maximising their lifespan. Routine inspections, cleaning procedures, and corrosion monitoring help identify potential issues early on, preventing costly repairs or replacements. By implementing a comprehensive maintenance strategy, operators can ensure the continued performance and reliability of GRP systems for years to come.
Innovations Driving Advancements in GRP Technology
The field of GRP manufacturing continues to evolve, driven by advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques. Innovations such as filament winding, centrifugal casting, and resin formulations have led to the development of GRP with enhanced properties, including higher pressure ratings, improved chemical resistance, and greater structural integrity. These technological advancements pave the way for the broader adoption of GRP in critical infrastructure projects worldwide.
Embracing the Future of Fluid Transportation with GRP Pipes
As societies strive for sustainable development and resilient infrastructure, the role of GRP becomes increasingly significant. With their unparalleled combination of strength, durability, and environmental sustainability, GRPs are poised to play a central role in meeting the evolving needs of water management, industrial processing, and energy production. By embracing the benefits of GRP and investing in its adoption, industries can build a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable future for generations to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GRP pipes offer a myriad of benefits that contribute to enhanced performance and efficiency in fluid transportation systems. From superior strength and corrosion resistance to hydraulic efficiency and environmental sustainability, GRP excels in various applications. By embracing pipes, industries can achieve cost savings, operational reliability, and environmental stewardship. As the demand for durable and sustainable infrastructure continues to rise, GRP emerges as a compelling solution for the challenges of tomorrow.












Comments